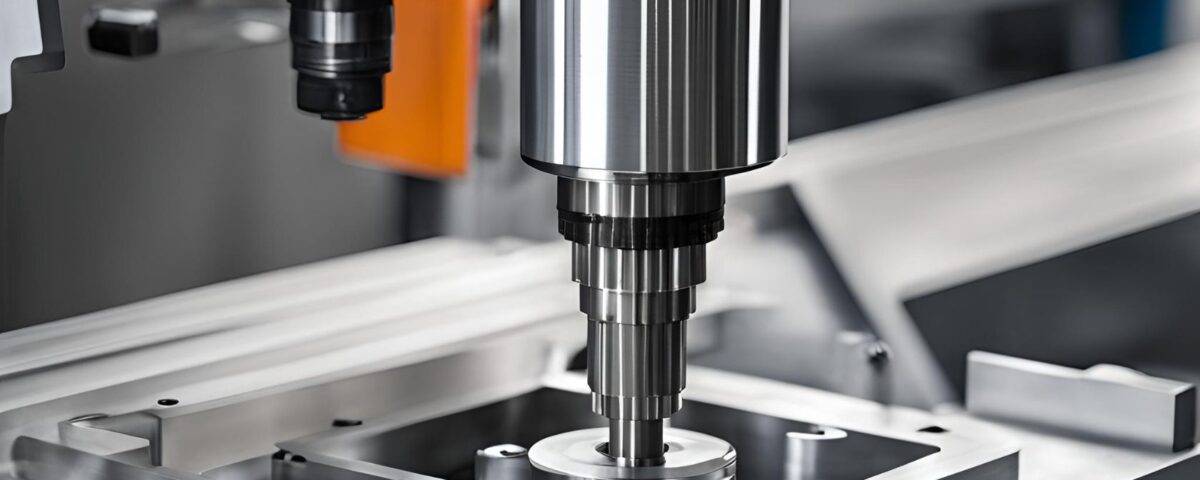
Exploring the Various Types of Five-Axis Machine Tools
26 June 2024
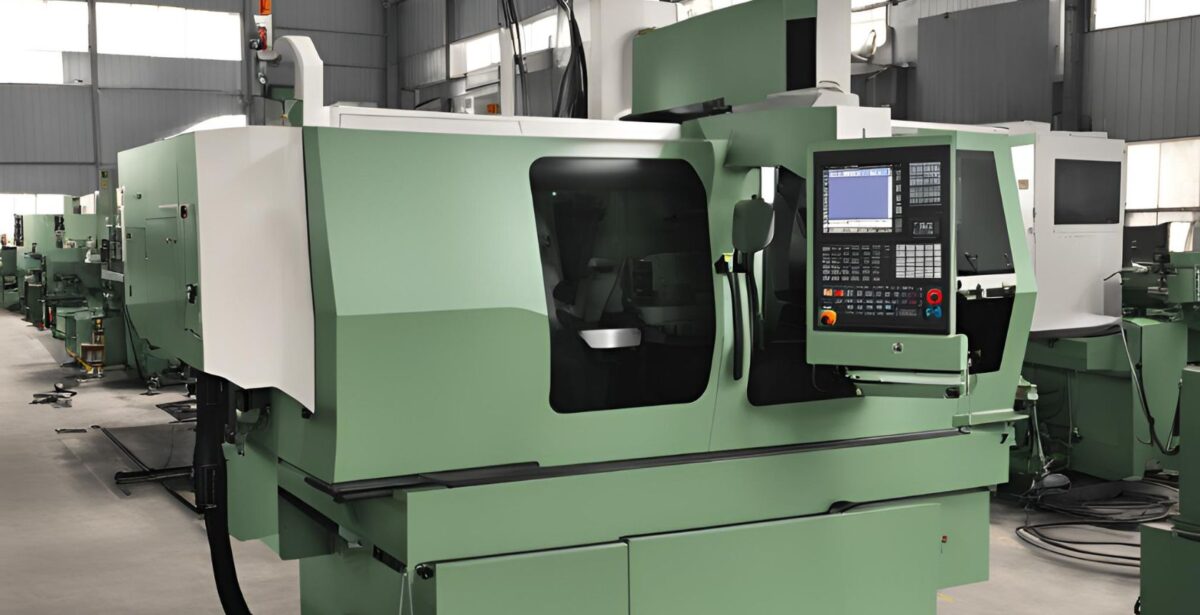
Understanding the CNC Lathe Machine Working Principle
2 July 2024Introduction
Ever found yourself puzzled by the myriad components of a CNC turning machine? I know the feeling. The sheer complexity can be overwhelming. But, worry not. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of each crucial part and its function. Trust me, it's not as daunting as it seems.
In this guide, we'll break down the main components of CNC turning machines. We'll also delve into supporting components and operational aspects, ensuring you get a comprehensive view of how these machines operate. This knowledge is crucial for anyone looking to master CNC machining or improve their existing setup.
What is CNC Turning Machines?
CNC turning machines, or lathes, are essential tools in manufacturing. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, which means these machines operate based on programmed commands. They excel at creating precise, cylindrical parts by rotating a workpiece while a stationary cutting tool shapes it.
The process begins with a raw material, usually a metal or plastic rod, secured in the spindle. As the spindle rotates, the cutting tool moves along defined paths, removing material to achieve the desired shape. This method allows for high precision and repeatability, making CNC turning ideal for producing complex components in large quantities. Whether in the automotive, aerospace, or medical industries, CNC turning machines are crucial for delivering high-quality, consistent parts.
What are the Main Components of CNC Turning Machines?
Spindle
The spindle is the powerhouse of a CNC turning machine. It is responsible for holding and rotating the workpiece with precision and stability. The spindle's performance directly affects the quality of the machined parts. Key factors like speed, torque, and rigidity are crucial for achieving high accuracy. In essence, the spindle's ability to maintain consistent rotational speed and alignment ensures smooth, precise cuts.
Chuck
The chuck is the gripping device that securely holds the workpiece in place during machining. It comes in various forms, such as three-jaw chucks, four-jaw chucks, and collet chucks, each offering different levels of precision and flexibility. A properly chosen chuck enhances the machine's ability to handle different sizes and shapes of materials, ensuring a firm hold without damaging the workpiece.
Tool Turret
The tool turret is a crucial component that houses multiple cutting tools. It can rotate to bring the required tool into position, allowing for quick and efficient tool changes during the machining process. This versatility significantly reduces downtime and increases productivity by enabling the machine to perform various operations without manual intervention.
Tailstock
The tailstock provides additional support for long workpieces, preventing deflection and ensuring precise machining. It can be moved along the bed to accommodate different lengths of materials. The tailstock is especially useful when performing operations that require high stability, such as drilling or threading. By maintaining the workpiece's alignment, the tailstock helps achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Bed
The bed is the foundation of the CNC turning machine. It supports all the other components and ensures the machine's structural integrity. The bed must be rigid and precisely aligned to prevent vibrations and maintain accuracy during machining. A well-designed bed provides stability and reduces the chances of misalignment, which can lead to defects in the finished product.

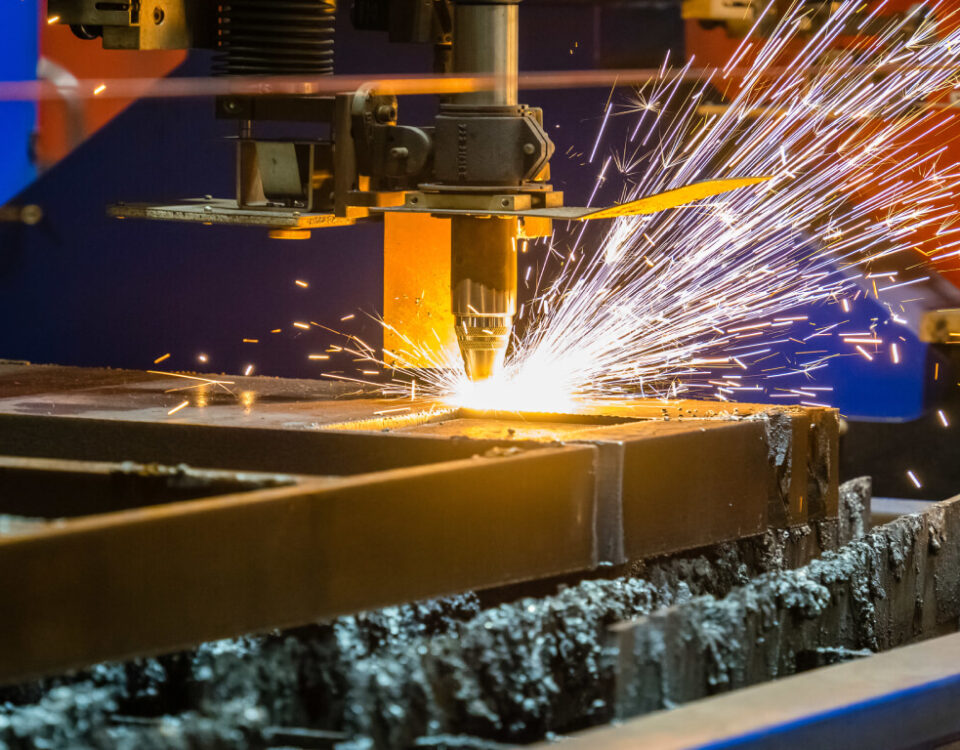
What are the Supporting Components?
Coolant System
The coolant system is a vital component in CNC turning machines. It serves multiple purposes, including cooling the cutting tool and workpiece, lubricating the cutting process, and flushing away chips and debris. By maintaining an optimal temperature, the coolant system helps prevent overheating and tool wear, thus extending the tool's lifespan and improving the surface finish of the machined parts. Proper coolant management is essential for efficient and accurate machining.
Chip Conveyor
The chip conveyor is designed to efficiently remove metal shavings and debris from the machining area. This not only keeps the workspace clean but also prevents chips from interfering with the machining process or damaging the machine. There are various types of chip conveyors, such as belt, drag, and magnetic conveyors, each suited to different types of materials and chip loads. A well-functioning chip conveyor enhances productivity and ensures smooth operation.
Control Panel
The control panel is the user interface of the CNC turning machine. It allows operators to program, monitor, and control the machining process. Modern control panels are equipped with advanced features such as touchscreens, real-time monitoring, and diagnostic tools. These features enable operators to easily set up and adjust machining parameters, troubleshoot issues, and optimize the machining process for better efficiency and precision. The control panel is the command center that makes CNC machining both intuitive and powerful.
Operational Aspects
Setup and Calibration
Setup and calibration are critical steps in ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of CNC turning machines. Proper setup involves aligning the workpiece, securing it in the chuck, and configuring the machine settings. Calibration ensures that the machine's measurements are accurate and consistent. This process includes setting tool offsets, verifying spindle speeds, and adjusting feed rates. Accurate setup and calibration minimize errors and ensure that the finished product meets the desired specifications.
Programming
Programming is the heart of CNC machining. It involves creating a set of instructions, or a program, that the CNC machine follows to perform the machining tasks. These instructions are typically written in G-code, which specifies the movements of the machine and the actions of the cutting tools. Effective programming requires a thorough understanding of the machining process, including tool paths, speeds, and feeds. Advanced programming techniques can optimize machining efficiency, reduce cycle times, and improve part quality.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to keep CNC turning machines running smoothly and to extend their lifespan. Maintenance tasks include lubricating moving parts, checking and replacing worn components, and ensuring that the machine is clean and free of debris. Scheduled maintenance can prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. Additionally, keeping the machine in good condition ensures consistent performance and high-quality output.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Machine Errors
Machine errors can be a major headache in CNC turning operations. These errors can arise from software glitches, hardware malfunctions, or operator mistakes. Common machine errors include misalignment, incorrect tool paths, and communication failures between the control panel and the machine components. To troubleshoot machine errors, it's crucial to regularly update software, perform routine checks on hardware, and ensure operators are well-trained. Keeping a detailed log of errors and solutions can also help in diagnosing recurring issues and implementing preventative measures.
Tool Wear
Tool wear is an inevitable aspect of CNC machining. As cutting tools are used, they gradually lose their sharpness, which can lead to poor cutting performance and diminished part quality. Signs of tool wear include increased cutting forces, poor surface finish, and dimensional inaccuracies. To mitigate tool wear, regularly inspect tools for wear patterns, replace tools at appropriate intervals, and use high-quality cutting fluids. Additionally, optimizing cutting parameters like speed, feed rate, and depth of cut can extend tool life.
Surface Finish Issues
Surface finish issues can significantly impact the quality and functionality of machined parts. These issues often stem from improper machining parameters, tool wear, or machine vibrations. Common surface finish problems include rough surfaces, chatter marks, and irregularities. To troubleshoot these issues, ensure that cutting tools are sharp and properly maintained, adjust machining parameters to optimal settings, and verify that the machine is stable and free of vibrations. Regular maintenance and calibration of the machine also play a vital role in preventing surface finish problems.

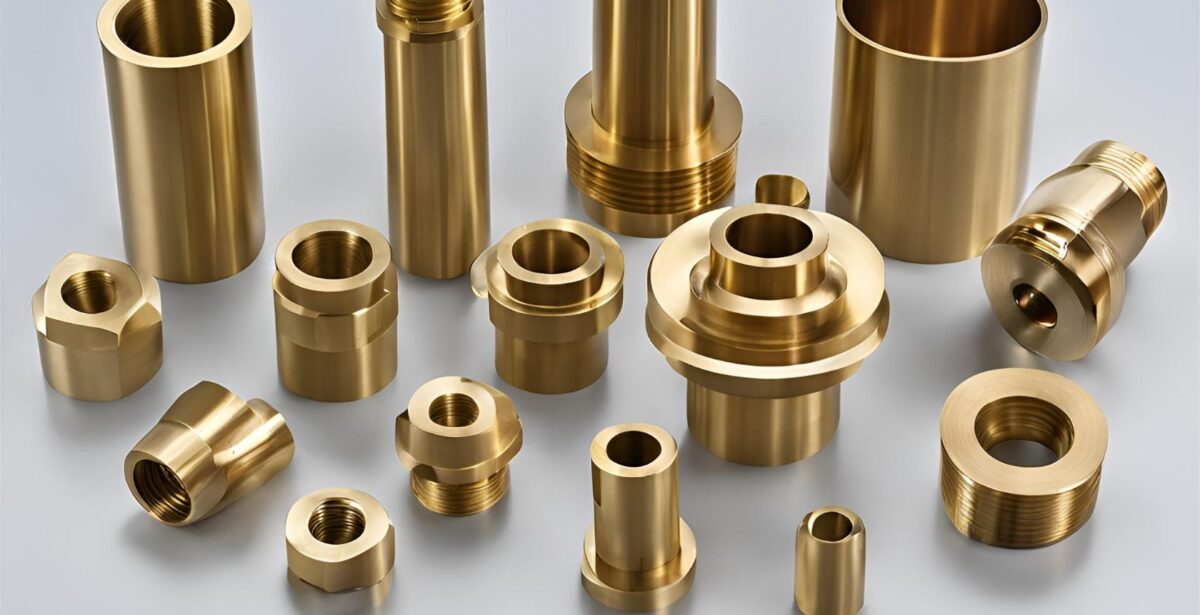
Applications of CNC Turning Machines
CNC turning machines are incredibly versatile and find applications across a wide range of industries. Their precision, efficiency, and ability to produce complex shapes make them indispensable in modern manufacturing. Let's dive into some of the key industries where CNC turning machines play a critical role.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, CNC turning machines are used to produce various components such as engine parts, transmission components, and suspension parts. These machines can manufacture intricate and high-precision parts that are essential for the performance and safety of vehicles. Components like pistons, gears, and shafts are commonly produced using CNC turning machines.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry demands components with the highest precision and reliability. CNC turning machines are ideal for producing parts like turbine blades, landing gear components, and structural parts. The ability to work with a variety of materials, including high-strength alloys and composites, makes CNC turning machines invaluable for aerospace applications.
Medical Industry
CNC turning machines are crucial in the medical industry for manufacturing components such as surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and dental prosthetics. These machines can produce small, intricate parts with tight tolerances, ensuring the highest quality and reliability. Materials like stainless steel, titanium, and medical-grade plastics are commonly used in CNC turning for medical applications.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, CNC turning machines are used to produce components such as connectors, enclosures, and heat sinks. The precision and repeatability of CNC turning ensure that electronic components meet the exact specifications required for high-performance devices. CNC turning machines can also handle delicate materials, making them suitable for manufacturing small and intricate electronic parts.
Military and Defense
CNC turning machines are used in the military and defense sectors to produce components for weapons, vehicles, and communication systems. These machines can manufacture parts with high precision and durability, essential for the demanding requirements of military applications. Materials like hardened steels and advanced composites are often used in CNC turning for defense purposes.
Industrial Machinery
CNC turning machines are also widely used in the production of industrial machinery components. This includes parts for pumps, valves, and industrial robots. The ability to produce durable and precise components ensures that industrial machinery operates efficiently and reliably.
Custom Manufacturing
CNC turning machines are not limited to large-scale production; they are also used for custom manufacturing and prototyping. They allow manufacturers to produce bespoke parts and components tailored to specific requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable for startups and R&D departments that need quick turnaround times and high-quality prototypes.
Conclusion
CNC turning machines are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, bringing precision, efficiency, and versatility to a wide range of industries. From automotive and aerospace to medical and electronics, these machines play a critical role in producing high-quality components with tight tolerances. Understanding the main components, supporting systems, operational aspects, and common issues of CNC turning machines can significantly enhance your ability to utilize these powerful tools effectively.
By mastering the setup and calibration, programming, and maintenance of CNC turning machines, you can optimize your production processes, reduce downtime, and improve the overall quality of your output. Additionally, being aware of common issues and troubleshooting techniques will help you maintain consistent performance and address problems promptly.
The applications of CNC turning machines are vast and varied, demonstrating their indispensable nature in today's manufacturing landscape. Whether you're producing intricate medical devices, robust automotive parts, or custom prototypes, CNC turning machines offer the precision and reliability needed to meet the demands of modern production.
As you continue to explore and utilize CNC turning machines, remember that staying informed and continuously improving your knowledge and skills will keep you at the forefront of manufacturing technology. Embrace the capabilities of these machines and unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation in your operations.
If you have any further questions or need more detailed information on any aspect of CNC turning machines, feel free to reach out. Happy machining!