Tooling and Fixture Design for Streamlined Manufacturing Operations
7 August 2024
Everything You Need to Know About Turned Metal CNC Machining Services
9 August 2024Are you struggling to understand CNC milling machines? Frustrated by the complexity and the sheer volume of information out there? You're not alone. In this beginner's guide, we'll demystify CNC milling machines, breaking down everything you need to know into manageable, easy-to-understand sections. By the end, you'll have a solid foundation to build on, whether you're a hobbyist or looking to start a career in CNC machining.
A CNC milling machine is a versatile and precise tool used in manufacturing to shape and cut materials with high accuracy, utilizing computer-controlled movements to follow pre-programmed instructions.
Curious to learn more? Let's dive into the world of CNC milling and uncover its potential.
What is CNC Milling?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a machining process that uses computerized controls and rotating multi-point cutting tools to progressively remove material from a workpiece, producing custom-designed parts or products. The CNC milling process can be performed in various directions on one or several axes, creating a wide range of shapes, slots, holes, and other necessary impressions.
The process begins with a digital 3D design of the desired part, created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design is then converted into CNC code (G-code and M-code) using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. The CNC machine reads these codes and translates them into the precise movements and operations needed to produce the part.
Unlike CNC turning, which is primarily used for producing cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, CNC milling involves the movement of the cutting tool against a stationary workpiece to remove material. This makes CNC milling particularly suited for creating complex geometries and intricate parts with high precision and repeatability.
Components of a CNC Milling Machine
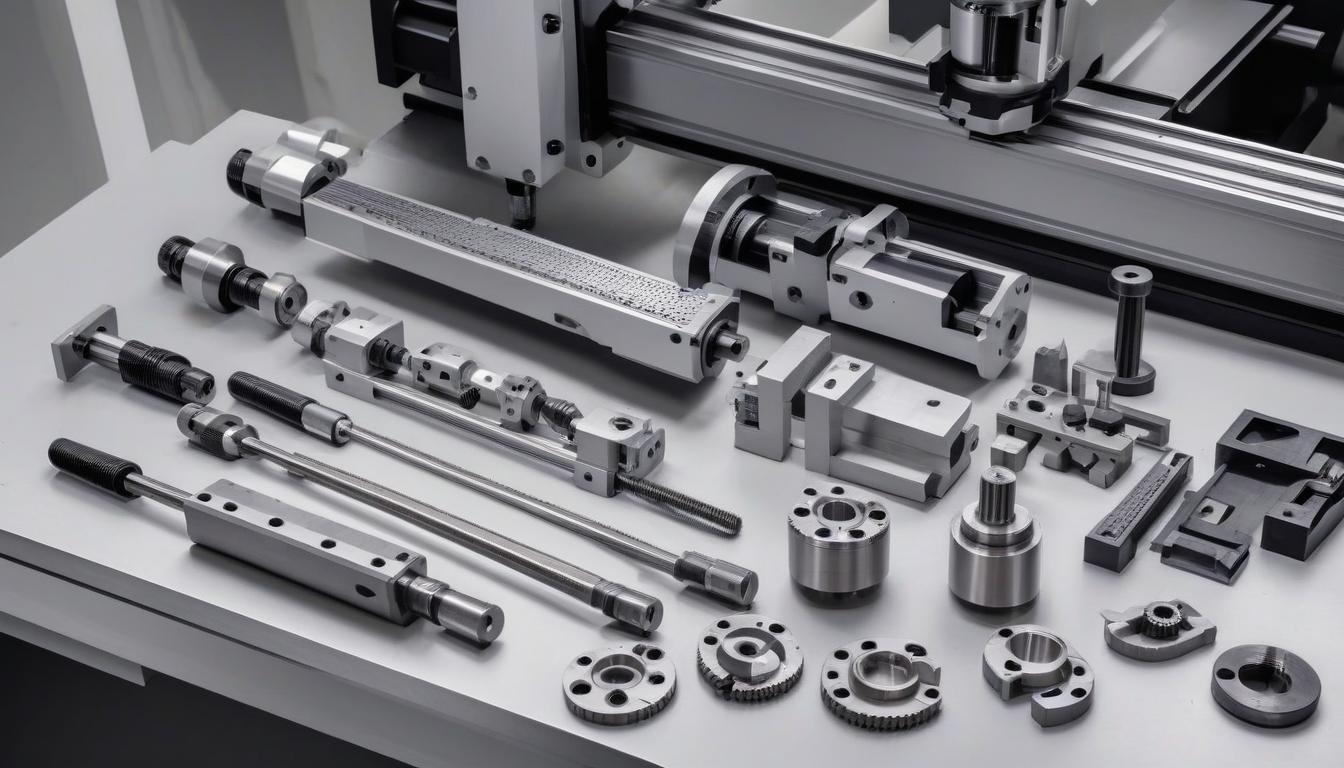

A CNC milling machine comprises several key components that work together to perform precise machining operations. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone starting with CNC milling. Here's a breakdown of the major parts:
Frame
The frame is the machine's backbone, providing structural support and stability. It houses and supports other components, ensuring the machine can withstand the forces generated during the milling process. Typically made from cast iron or steel, the frame minimizes vibrations and enhances machining accuracy.
Spindle
The spindle is the rotating component that holds and drives the cutting tool. It's powered by an electric motor and can rotate at varying speeds, depending on the material and the specific operation being performed. The spindle's precision and power are critical for achieving high-quality cuts and finishes.
Table
The table is the platform where the workpiece is secured during machining. It moves along different axes (usually X, Y, and Z) to position the workpiece correctly relative to the cutting tool. Tables can have T-slots for clamping workpieces or fixtures and may include additional features like vacuum chucks or magnetic plates for secure workholding.
Control Panel
The control panel is the interface through which the operator inputs commands and controls the machine. It includes a display screen, keyboard, and various buttons and knobs for operating the CNC system. Modern CNC machines often feature touchscreens and advanced interfaces for more intuitive control.
Other Essential Components
Tool Changer
The tool changer is a device that automatically swaps cutting tools during the machining process. It allows for continuous machining without manual intervention, increasing efficiency and productivity. Tool changers can hold multiple tools and are programmed to select and change tools as needed for different operations.
Linear Guides and Ball Screws
Linear guides and ball screws are critical for precise movement and positioning of the machine's components. Linear guides provide smooth, accurate motion along the machine's axes, while ball screws convert rotational motion into linear motion with high precision. These components ensure that the machine can move accurately and consistently, resulting in precise cuts and high-quality finishes.
Cooling System
The cooling system helps dissipate heat generated during the machining process, preventing overheating and maintaining the integrity of both the machine and the workpiece. It typically includes a coolant pump, reservoir, and nozzles that direct coolant onto the cutting area. Effective cooling is essential for prolonging tool life and ensuring consistent machining performance.
Enclosure
The enclosure is a safety feature that surrounds the working area of the CNC milling machine. It protects the operator from moving parts, flying debris, and coolant spray. Enclosures also help contain noise and reduce the environmental impact of the machining process.
How CNC Milling Machines Work
CNC milling machines are marvels of modern engineering, combining computer technology with precise machining capabilities. Understanding how these machines work involves a step-by-step look at the entire process, from design to final product. Here’s an in-depth explanation of how CNC milling machines operate:
Step-by-Step Process
- Design the Part
The process begins with creating a digital 3D model of the desired part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This model includes all the specifications and dimensions necessary for machining. - Convert the Design to CNC Code
The CAD model is then imported into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, which translates the design into CNC code, primarily G-code and M-code. G-code dictates the movement and positioning of the machine's components, while M-code handles auxiliary functions such as coolant control and tool changes. - Setup the Machine
Before machining begins, the workpiece is securely clamped onto the machine's table, and the appropriate cutting tool is installed in the spindle. The machine is then calibrated to ensure accurate positioning and alignment of the workpiece and tool. - Load the CNC Program
The CNC code generated by the CAM software is loaded into the machine’s control panel. This program contains all the instructions the machine needs to execute the machining operations. - Execute the Machining Operations
The machine follows the CNC code to perform the machining operations. The spindle rotates the cutting tool at high speeds, and the table moves the workpiece along the X, Y, and Z axes as required. The cutting tool removes material from the workpiece to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. - Monitor and Adjust
Throughout the machining process, the operator monitors the machine’s performance, making adjustments as necessary to ensure accuracy and quality. This may involve tweaking the feed rate, spindle speed, or tool path. - Finishing and Inspection
Once machining is complete, the finished part is removed from the table. It may undergo additional finishing processes, such as deburring or polishing, to achieve the desired surface quality. Finally, the part is inspected for accuracy and quality assurance.
Explanation of CNC Programming
G-Code and M-Code
- G-Code: G-code is the language that controls the movements of the CNC milling machine. It specifies the paths the cutting tool will follow, including linear and circular movements, as well as positioning commands. Examples of G-code commands include:
- G01: Linear interpolation (cutting in a straight line)
- G02: Circular interpolation, clockwise
- G03: Circular interpolation, counterclockwise
- M-Code: M-code handles miscellaneous functions and auxiliary operations. These commands control non-movement aspects of the machining process, such as:
- M00: Program stop
- M03: Spindle on, clockwise
- M08: Coolant on
Role of the Operator
Even though CNC milling machines are highly automated, the operator plays a crucial role in ensuring successful machining operations:
- Setup: The operator is responsible for setting up the machine, which includes clamping the workpiece, installing the cutting tool, and calibrating the machine.
- Programming: While the CAM software generates the CNC code, the operator must understand and verify the code to ensure it accurately represents the desired operations.
- Monitoring: During machining, the operator monitors the machine’s performance, looking out for any issues such as tool wear, overheating, or deviations from the desired dimensions.
- Troubleshooting: If problems arise, the operator must be able to troubleshoot and resolve them to maintain the quality and efficiency of the machining process.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance tasks, such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of machine components, are essential to keep the CNC milling machine in optimal working condition.
Types of CNC Milling Machines
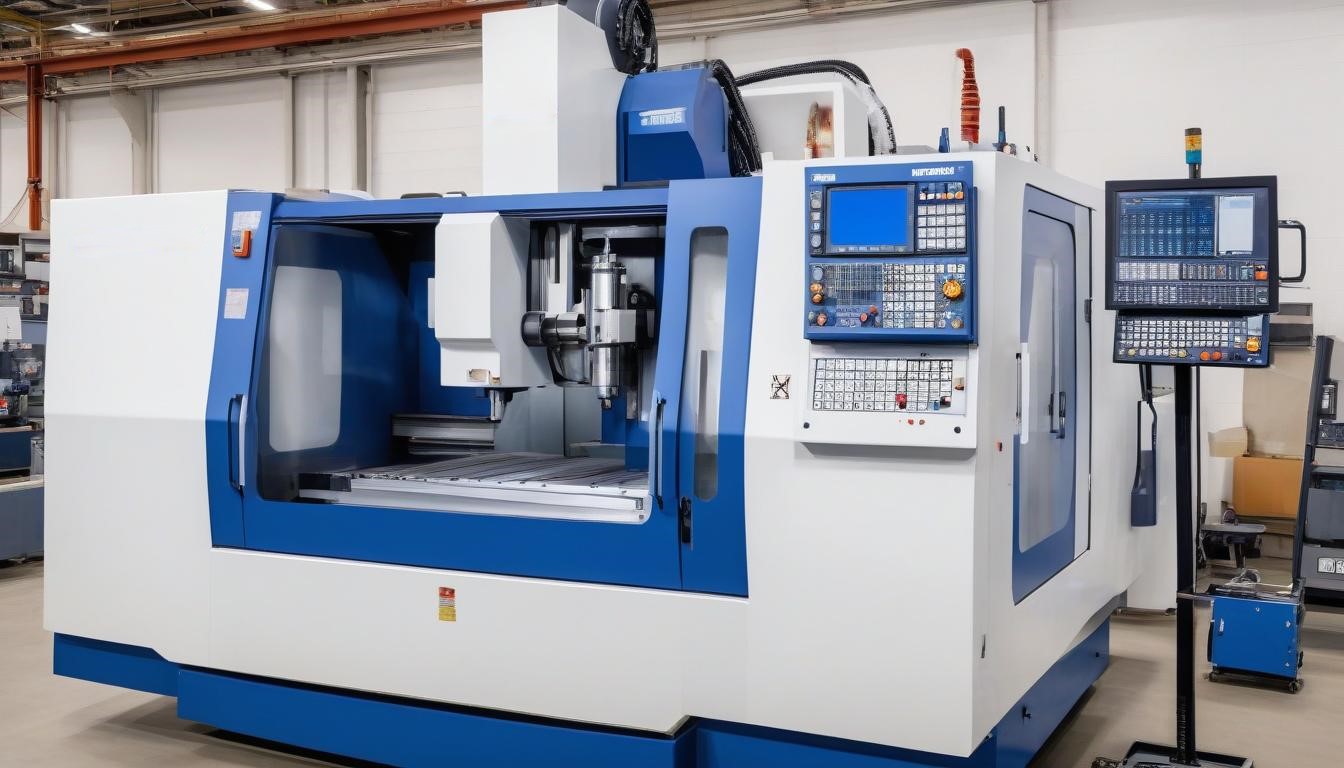

CNC milling machines come in various configurations, each designed to meet specific machining requirements and to handle different levels of complexity and precision. Understanding the different types of CNC milling machines is essential for selecting the right machine for your needs. Here are the main types:
Vertical CNC Milling Machines
Vertical CNC milling machines have a vertically oriented spindle, which allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from above. These machines are widely used for their versatility and ability to perform various operations, such as drilling, tapping, and contouring.
Key features include:
- Vertical Spindle Orientation: The spindle is aligned vertically, making it ideal for tasks that involve cutting and shaping the top surface of the workpiece.
- Table Movement: The table can move in the X and Y axes, while the spindle moves along the Z axis, allowing for precise three-dimensional machining.
- Applications: Vertical CNC milling machines are commonly used in manufacturing automotive components, aerospace parts, and complex molds.
Horizontal CNC Milling Machines
Horizontal CNC milling machines have a horizontally oriented spindle. This design allows for more efficient removal of material and better chip evacuation, making them suitable for heavy-duty cutting operations.
Key features include:
- Horizontal Spindle Orientation: The spindle is aligned horizontally, which helps in reducing the buildup of chips and allows for faster cutting speeds.
- Table Movement: The table moves in the X and Y axes, while the spindle moves along the Z axis. Some horizontal mills also have a rotating table to access different sides of the workpiece.
- Applications: Horizontal CNC milling machines are ideal for machining large and heavy workpieces, such as engine blocks, transmission cases, and structural components.
5-Axis CNC Milling Machines
5-axis CNC milling machines are advanced machining centers capable of moving the cutting tool along five different axes simultaneously. This capability allows for the creation of highly complex and intricate parts.
Key features include:
- Simultaneous 5-Axis Movement: The cutting tool can move along the X, Y, and Z axes, and rotate around the A and B axes, enabling access to the workpiece from multiple angles.
- Complex Geometry Machining: These machines can produce parts with intricate geometries, undercuts, and compound angles that would be impossible or highly challenging with 3-axis or 4-axis machines.
- Applications: 5-axis CNC milling machines are used in industries requiring high precision and complexity, such as aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and advanced research and development.
Other Specialized CNC Milling Machines
- CNC Gantry Mills: These machines feature a gantry frame with a bridge-like structure, allowing for the machining of very large and heavy workpieces. They are commonly used in the aerospace and shipbuilding industries.
- CNC Bed Mills: Bed mills have a stationary table and a vertically moving spindle head, making them suitable for heavy and large workpieces that require precise vertical movements.
- CNC Knee Mills: These machines have a vertically adjustable table that rests on a knee and can be moved up and down. They are often used for smaller, more detailed workpieces and are popular in educational and prototyping environments.
Choosing the Right CNC Milling Machine
Selecting the appropriate CNC milling machine depends on several factors:
- Workpiece Size and Weight: Consider the dimensions and weight of the parts you will be machining. Horizontal mills or gantry mills might be necessary for large and heavy workpieces.
- Complexity of the Parts: For intricate and highly detailed parts, a 5-axis CNC milling machine may be required.
- Material: The type of material being machined can influence the choice of machine. Horizontal mills are better suited for heavy cutting in tough materials, while vertical mills can handle a variety of materials with ease.
- Production Volume: High-volume production may require machines with automated tool changers and advanced features to maximize efficiency.
Materials Used in CNC Milling
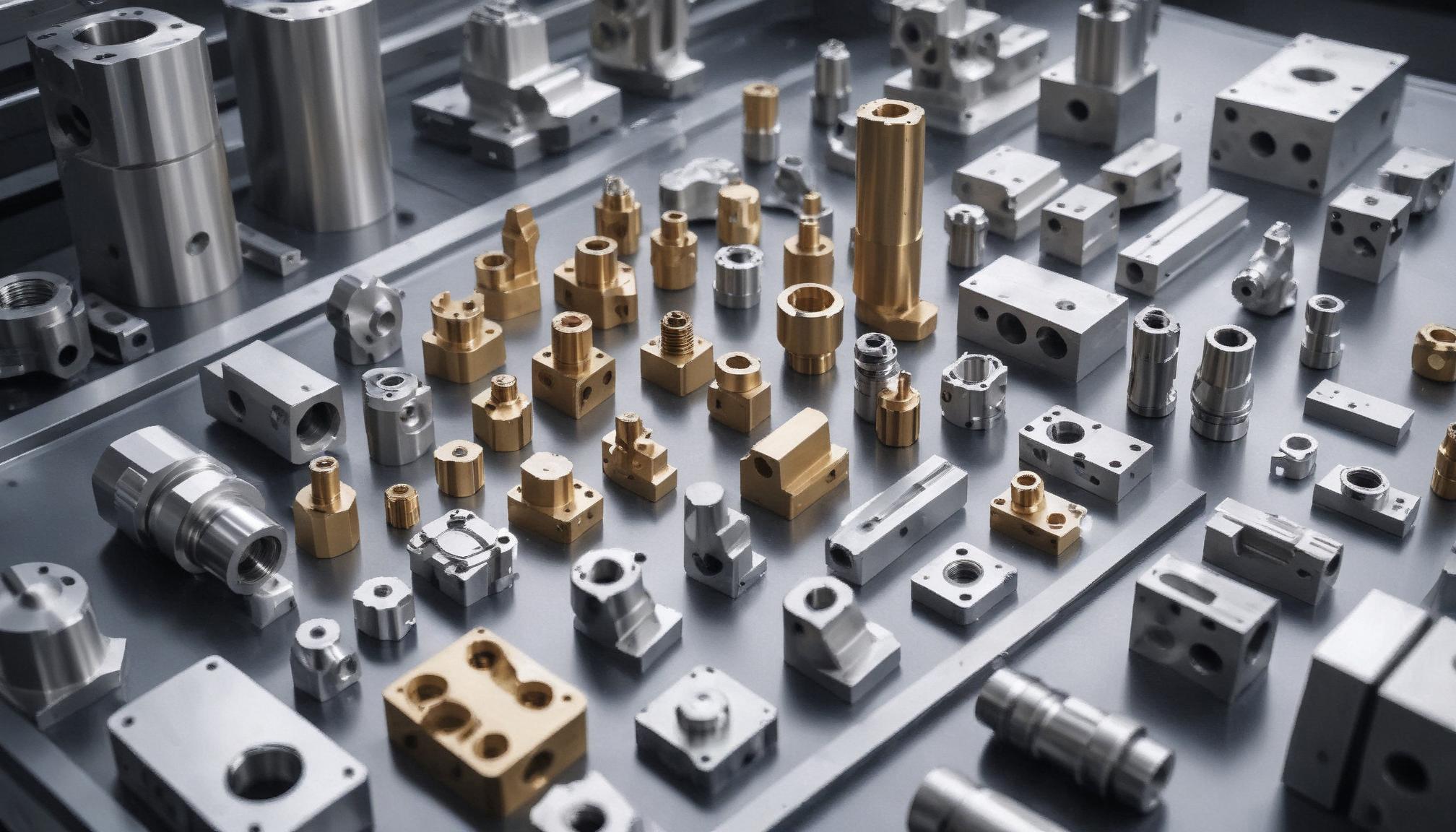
CNC milling machines can work with a wide range of materials, each offering unique properties and applications. Understanding the materials used in CNC milling is crucial for selecting the right one for your project. Here’s a breakdown of the most common materials:
Metals
Metals are the most frequently machined materials due to their strength, durability, and versatility. Common metals used in CNC milling include:
Aluminum:
- Properties: Lightweight, strong, and highly machinable, with excellent corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, and consumer electronics.
Steel:
- Properties: Extremely strong and durable, with varying properties depending on the alloy. Can be hardened for wear resistance.
- Applications: Structural components, machinery parts, and tools.
Stainless Steel:
- Properties: Corrosion-resistant, strong, and durable. Difficult to machine compared to other metals.
- Applications: Medical devices, food processing equipment, and marine applications.
Titanium:
- Properties: Strong as steel but much lighter, with excellent corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Applications: Aerospace components, medical implants, and high-performance automotive parts.
Brass:
- Properties: Easy to machine, good corrosion resistance, and attractive finish. Excellent for precision components.
- Applications: Electrical connectors, plumbing fittings, and decorative parts.
Plastics
Plastics are widely used in CNC milling for their versatility, ease of machining, and unique properties. Common plastics include:
Delrin (POM):
- Properties: High strength, low friction, excellent dimensional stability, and resistance to wear and chemicals.
- Applications: Gears, bearings, and bushings.
ABS:
- Properties: Strong, impact-resistant, and easy to machine. Good dimensional stability and surface finish.
- Applications: Enclosures, prototypes, and consumer products.
Polycarbonate:
- Properties: High impact resistance, optical clarity, and good thermal stability.
- Applications: Safety guards, lenses, and high-performance components.
Nylon:
- Properties: Strong, wear-resistant, and low friction. Absorbs moisture, which can affect dimensional stability.
- Applications: Gears, bearings, and structural components.
Composites
Composites combine two or more materials to create a material with superior properties. Common composites used in CNC milling include:
Carbon Fiber:
- Properties: Extremely strong and lightweight, with high stiffness and excellent fatigue resistance.
- Applications: Aerospace components, sporting goods, and high-performance automotive parts.
Fiberglass:
- Properties: Strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant, with good thermal insulation properties.
- Applications: Boat hulls, automotive components, and structural parts.
Wood
While less common in industrial applications, wood is still used in CNC milling, especially in furniture making, mold patterns, and artistic projects. Common types of wood include:
Hardwoods (e.g., Oak, Maple):
- Properties: Dense, strong, and durable, with a fine grain that allows for detailed machining.
- Applications: Furniture, cabinetry, and flooring.
Softwoods (e.g., Pine, Cedar):
- Properties: Lightweight, easy to machine, and less dense than hardwoods.
- Applications: Construction, mold patterns, and decorative items.
Choosing the Right Material
Selecting the right material for your CNC milling project depends on several factors:
- Mechanical Properties: Consider the strength, hardness, wear resistance, and impact resistance required for the part.
- Thermal Properties: Evaluate the material’s ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling.
- Chemical Resistance: Assess the material’s resistance to corrosion, solvents, and other chemicals.
- Machinability: Determine how easy the material is to machine, including its ability to hold tight tolerances and achieve a good surface finish.
- Cost: Balance the material’s cost with its performance characteristics to ensure cost-effective production.
Advantages of CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines offer several distinct advantages over traditional machining methods, making them a preferred choice for many manufacturing and prototyping applications. Here are the key benefits:
Precision and Accuracy
- High Tolerances: CNC milling machines are capable of achieving extremely tight tolerances and precise measurements, often down to micrometers. This level of accuracy is essential for producing high-quality parts and components with consistent dimensions.
- Repeatability: Once a CNC milling machine is programmed, it can reproduce the same part with identical specifications repeatedly, ensuring uniformity across all produced items. This repeatability is crucial for high-volume production runs and maintaining quality control.
Efficiency and Speed
- Reduced Production Time: CNC milling machines can operate continuously without the need for manual intervention, significantly reducing production time compared to traditional machining methods. Automation speeds up the process, allowing for faster turnaround on projects.
- Rapid Prototyping: CNC milling enables quick production of prototypes and custom parts, accelerating the product development cycle and allowing for faster iteration and refinement of designs.
Flexibility in Design
- Complex Geometries: CNC milling machines can create complex and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with manual machining. The ability to execute detailed and sophisticated patterns makes them ideal for producing complex components.
- Versatile Material Handling: CNC milling machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and wood. This versatility allows manufacturers to use CNC milling for various applications and industries.
Reduced Human Error
- Minimized Manual Handling: By automating the machining process, CNC milling machines reduce the risk of human error that can occur with manual operations. The machine follows precise instructions from the CNC program, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Consistent Quality: Automated control and monitoring systems help maintain high-quality standards throughout the production process, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring that each part meets the specified requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Lower Labor Costs: CNC milling machines require fewer operators and less manual intervention compared to traditional machining methods, leading to reduced labor costs. The automation also means fewer mistakes and less waste, contributing to overall cost savings.
- Efficient Tool Usage: CNC machines are designed to optimize tool usage, minimizing wear and tear and extending the life of cutting tools. This efficiency reduces the need for frequent tool replacements and lowers maintenance costs.
Enhanced Safety
- Operator Protection: CNC milling machines are equipped with safety enclosures and automated controls that protect operators from moving parts and flying debris. This enhanced safety reduces the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
- Reduced Manual Handling: The automation of the machining process reduces the need for manual handling of tools and workpieces, further minimizing safety risks associated with traditional machining methods.
Customization and Adaptability
- Easy Reprogramming: CNC milling machines can be quickly reprogrammed to produce different parts or modify existing designs. This adaptability allows manufacturers to respond to changing market demands and customer requirements with ease.
- Rapid Adjustments: Design changes and adjustments can be implemented swiftly, enabling manufacturers to experiment with new ideas and improve product designs without significant delays or costs.
Applications of CNC Milling
CNC milling is widely used across various industries, including:
- Automotive: Manufacturing engine components, gears, and other precision parts.
- Aerospace: Producing aircraft components, turbine blades, and structural parts.
- Medical: Creating surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics.
- Electronics: Fabricating circuit boards, enclosures, and other electronic components.
Conclusion
CNC milling machines represent a powerful and versatile tool in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and flexibility. By understanding the fundamentals of CNC milling, from selecting the right machine to mastering programming and adhering to safety protocols, you can unlock a wide range of possibilities for producing high-quality parts and components. Whether you’re embarking on a new project or refining existing processes, CNC milling provides the accuracy and capability needed to meet complex demands and drive innovation across various industries. Embrace the potential of CNC milling and take advantage of its benefits to achieve outstanding results in your machining endeavors.