How Sheet Metal Fabrication Shapes Industries
8 November 2024
Exploring Seven Key Techniques in Thread Processing
14 November 2024Rapid prototyping is revolutionary in the dynamic field of product development. It makes it possible for engineers, designers, and inventors to realize their concepts more quickly, effectively, and at a fraction of the price of conventional manufacturing. Before a product reaches the final phases of production, rapid prototyping is a flexible technique that helps businesses in a variety of industries conceptualize concepts, find design faults, and improve functionality. Rapid prototyping is changing how things are developed, tested, and improved in a variety of industries, including healthcare, fashion, automotive, and aerospace. Let's examine this procedure in more detail and the numerous advantages it provides for different industries.
What Exactly is Rapid Prototyping?
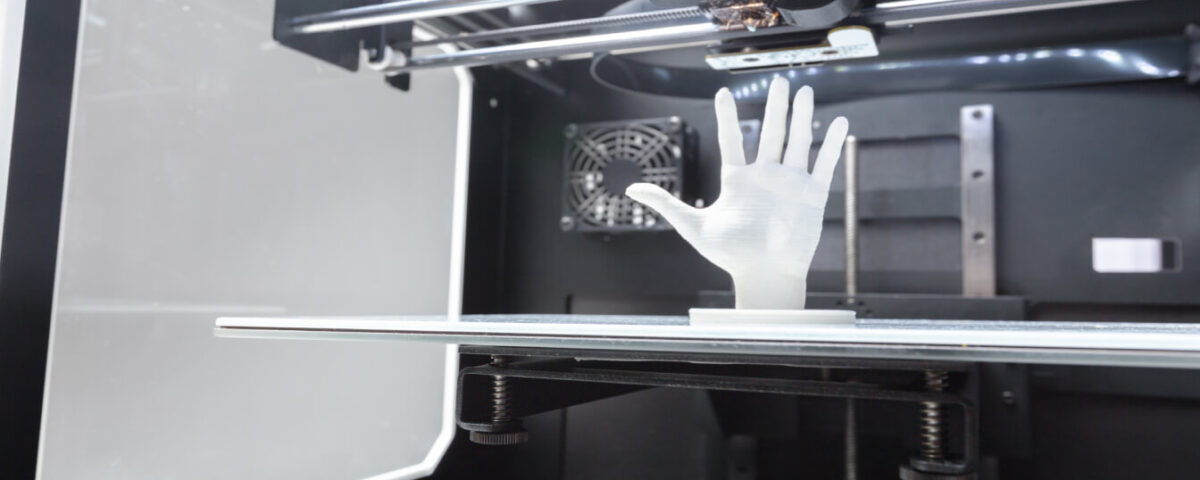
The process of rapidly producing a physical model or component from a digital design is known as rapid prototyping. Rapid prototyping combines 3D printing and other cutting-edge techniques to turn a digital model into a physical thing, layer by layer, in hours or days as opposed to weeks, unlike traditional manufacturing processes that can be expensive and time-consuming. From basic visual models to completely working components, these prototypes enable engineers and designers to rapidly test ideas, improve designs, and make necessary modifications. Rapid prototyping has therefore become crucial for businesses trying to cut down on development time, decrease mistakes, and boost overall creativity.
Key Benefits of Rapid Prototyping in Product Development
Rapid prototyping has shifted product development dynamics, offering several significant advantages that traditional methods cannot match:
- Speed and Efficiency: Conventional prototyping, which frequently requires costly labor and tools, can take weeks or months. Some parts can be made in a matter of hours thanks to rapid prototyping, which drastically cuts down on this time. Businesses may improve designs and launch goods more quickly thanks to this speed.
- Cost Reduction: Significant savings can be achieved by doing away with the requirement for molds, specialized tools, and numerous machining procedures. Rapid prototyping allows businesses to quickly make changes and avoid the high expenses of retooling by using CAD files to build several copies of a prototype.
- Improved Functionality and Product Testing: Rapid prototyping can create prototypes that can be used in real-world settings and for functionality testing. Designers and engineers can analyze a product's performance, spot problems, and improve the design as necessary. Higher product quality and fewer design flaws are ensured by this procedure.
- Greater Flexibility and Creativity: Rapid prototyping promotes creativity and exploration because there are less time and financial constraints. Without settling on a single course too early in the development process, businesses can experiment with various forms, textures, materials, and design concepts. This flexibility fosters the development of original ideas and goods.
- Engagement of Customers and Stakeholders: Rapid prototyping can improve how well businesses convey ideas. With a tangible model in hand, team members, clients, and stakeholders may see the finished product, offer suggestions, and have a significant impact on the development process.
The Process of Rapid Prototyping: From Digital Design to Physical Model
The rapid prototyping process typically follows several steps:
-
Conceptualization: The product development team generates ideas and creates initial designs based on their goals, customer needs, and market requirements.
-
3D Modeling: Using CAD software, designers create detailed digital models of the product. This step often involves multiple iterations as the team refines the design before creating a physical prototype.
-
Prototype Creation: The CAD model is then transferred to a 3D printer or another rapid prototyping machine. Layer by layer, the machine builds the model using materials such as plastic, resin, or metal, depending on the desired characteristics.
-
Testing and Feedback: Once the prototype is complete, it undergoes testing. This stage may involve assessing physical properties, functionality, and aesthetic elements. Feedback gathered from testing informs further design refinements.
-
Iteration and Refinement: Based on the feedback, designers revise the model, and the process repeats until the final product meets the necessary specifications and standards.
Real-World Applications of Rapid Prototyping Across Different Industries
The versatility of rapid prototyping allows it to benefit many industries. Here’s how it’s making a difference across a range of fields:
-
Automotive Industry: From full-scale vehicle models to minor elements like engine components, automakers test everything via rapid prototyping. By creating precise models quickly, the technology helps automakers find possible defects, improve designs, and save production costs. Prototypes of dashboards, automobile interiors, and other aesthetically pleasing elements, for instance, enable designers to assess usability and ergonomics prior to mass production.
Healthcare and Medical gadgets: The development of surgical instruments, medical gadgets, and even prosthetic limbs has benefited greatly from rapid prototyping. Custom prosthetics and implants, for example, can be made to fit each patient's particular anatomy. Furthermore, doctors can rehearse complicated surgeries using 3D-printed surgical models, which could enhance patient safety and surgical results. Prototyping helps medical device firms test for functionality and regulatory compliance.
Aerospace and Defense: To design, test, and enhance the performance of components that must endure severe stress and precise specifications, aerospace businesses use rapid prototyping. Prototypes for aerospace frequently go through extensive testing to make sure the materials and design decisions satisfy the exacting requirements of the sector. Prototyping enables the development of components that optimize fuel efficiency while preserving structural integrity by using lightweight yet robust materials.
Consumer Electronics: Rapid prototyping is used by electronics makers to assess the ergonomics, design aesthetics, and assembly needs of devices such as wearables, computers, and smartphones. Engineers make sure that items work as intended and satisfy the aesthetic needs of contemporary consumers by testing them on real models. Because rapid prototyping enables quick iterations based on client feedback, it also supports user-centered design.
Fashion and Footwear: Rapid prototyping is being used more and more in the fashion sector to create unique shoes, jewelry, and accessories. Prototypes of fashion goods can be made by designers to evaluate functioning and design aspects, providing customers with more individualized and distinctive products. Rapid prototyping is utilized in the footwear industry to develop limited-edition styles and test ergonomics and aesthetics.
Architecture and Construction: To produce scale models of structures and structural components, architects employ fast prototyping. Stakeholders can use these models to visualize ideas and make well-informed decisions regarding structural integrity, utility, and aesthetics. Furthermore, rapid prototyping enhances construction projects' accuracy and efficiency by enabling architects to test structural elements before incorporating them into finished structures.
How Rapid Prototyping Fuels Innovation
Rapid prototyping encourages companies to think creatively and embrace an experimental mindset. Here’s how rapid prototyping is transforming product development:
-
Accelerating Time to Market: In highly competitive markets where maintaining an advantage is critical, faster prototyping results in faster product releases. Compared to typical manufacturing procedures, rapid prototyping enables businesses to iterate quickly, improve designs, and launch products more quickly.
-
Reducing Production Risks: The likelihood of expensive mistakes during mass production is decreased by detecting and fixing design defects during the prototyping stage. Businesses make sure the product satisfies performance requirements and customer expectations by developing working prototypes.
-
Promoting Cross-Functional Collaboration: Design, engineering, and production teams can work together more easily thanks to rapid prototyping. Because prototypes are physical, teams can evaluate a product's shape and functionality simultaneously, which enhances communication and produces more unified outcomes.
-
Encouraging Iterative Design: Rapid prototyping encourages iterative development, in contrast to older approaches that could restrict the quantity of prototypes because of financial or schedule limitations. As teams iterate designs in response to testing, feedback, and fresh insights, this methodology promotes continuous improvement.
Addressing Challenges in Rapid Prototyping
While rapid prototyping offers many benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges:
-
Material Restrictions: Prototyping materials aren't necessarily appropriate for the finished product. Plastic prototypes could not function as well as metal final versions, therefore designers need to take these variations into consideration throughout the manufacturing stage.
-
Limitations on Precision: Certain rapid prototyping methods might not be able to produce detailed parts with the accuracy required. Many applications might benefit from 3D printing, however in order to fulfill quality standards, highly intricate components could need extra finishing stages.
-
Cost-Scale Balancing: While rapid prototyping is less expensive than traditional tooling, it can still be costly to create numerous or intricate prototypes. In some situations, businesses must decide if the speed and flexibility outweigh the additional expenses.
The Future of Rapid Prototyping: Enhanced Materials and AI Integration
The future of rapid prototyping looks promising, with ongoing advancements in materials and technology. Here’s what we can expect in the coming years:
- Advanced Materials: To improve durability, flexibility, and finish, new materials are being developed for rapid prototyping. More functional and realistic prototypes that closely resemble finished goods will be made possible by improved material alternatives.
- AI-Driven Design Optimization: Rapid prototyping software can optimize designs for cost, weight, and strength by integrating AI. By recommending ideal structures, using less material, and increasing overall efficiency, AI-powered simulations and generative design can improve the prototyping process.
-
Increased Accessibility: As 3D printing technology becomes more affordable and user-friendly, rapid prototyping will become accessible to small businesses and startups, democratizing product development and encouraging more widespread innovation.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is revolutionizing businesses by making it possible to design products quickly, effectively, and affordably. Its adaptability enables regular iteration and improvement, enabling businesses to launch better, more inventive goods more quickly than ever before. Rapid prototyping will become ever more important in promoting innovation, creativity, and teamwork across various industries as technology develops. Rapid prototyping is expected to open up new avenues in the future, making it an effective tool for manufacturers and innovators everywhere.